Modeling & Multi-Scale Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging has made it possible to visualise brain structure and function with unprecedented spatial accuracy. We at the Translational Neurotechnology Lab use high-resolution structural MRI to model the volume conduction of electrical activity and functional MRI to pursue novel multi-scale layer-based analyses.
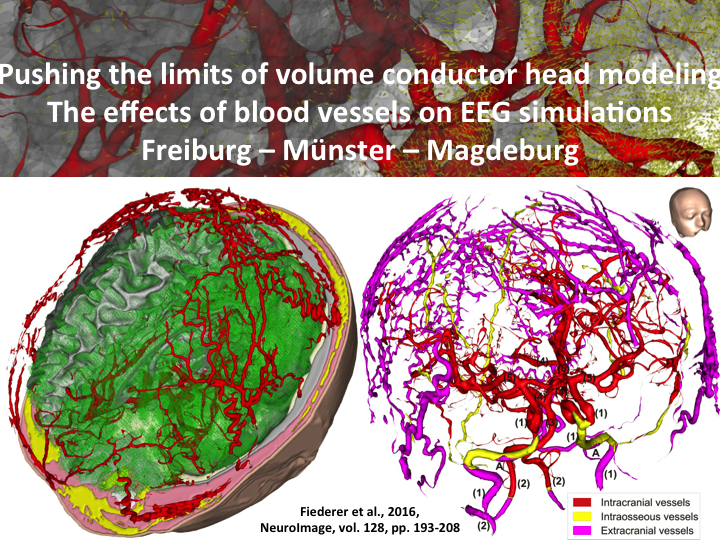
High-resolution volume conductor imaging
Affiliated researchers: PD Dr. Tonio Ball, Dr. Lukas Fiederer
Modeling the volume conduction of electrical activity is a crucial component for understanding the spatial aspects of both electrical neuronal activity and electrical brain stimulation. Be it using standard clinical MRI or high-end 7 Tesla MRI, our modeling pipelines try to catch the smallest details as these can have considerable influence on results.
Spatial multi-scale analyses of fMRI data
Affiliated researchers: PD Dr. Tonio Ball, Roland Berkemeier, Dr. Philipp Kellmeyer
- Research motivation: Conventional analyses of fMRI data uses single-filter smoothing, typically with Gaussian filters ranging from 4-12 mm at Full-width Half Maximum (FWHM). Previous research from our group (Ball et al., 2012) has shown that varying the spatial observation scale reveals substantial differences in fMRI response between smoothing filters of different sizes. Given almost all fMRI studies only use a single filter size for data analysis, ignoring this spatial-scale-dependent variation of fMRI responses could substantially affect the validity of fMRI research.
- Research goals: In this project we aim to
(1) Further study the variations depending on the spatial scale of fMRI responses across different task-based experiments (e.g. in speech);
(2) To develop surface-constrained smoothing methods to eliminate some inherent methodological problems of volumetric smoothing kernels
(3) Apply these methods to connectivity analyses of fMRI data
Affiliated publications:
- Mutschler, Isabella, Tonio Ball, Ursula Kirmse, Birgit Wieckhorst, Michael Pluess, Markus Klarhöfer, Andrea H. Meyer, Frank H. Wilhelm, and Erich Seifritz. “The Role of the Subgenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex and Amygdala in Environmental Sensitivity to Infant Crying.” PLOS ONE 11, no. 8 (August 25, 2016): e0161181. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161181.
- Fiederer, L. D. J., J. Lahr, J. Vorwerk, F. Lucka, A. Aertsen, C. H. Wolters, A. Schulze-Bonhage, and T. Ball. “Electrical Stimulation of the Human Cerebral Cortex by Extracranial Muscle Activity: Effect Quantification With Intracranial EEG and FEM Simulations.” IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 63, no. 12 (December 2016): 2552–63. doi:10.1109/TBME.2016.2570743.
- Fiederer, L. D. J., J. Vorwerk, F. Lucka, M. Dannhauer, S. Yang, M. Dümpelmann, A. Schulze-Bonhage, A. Aertsen, O. Speck, C. H. Wolters, and T. Ball. “The Role of Blood Vessels in High-Resolution Volume Conductor Head Modeling of EEG.” NeuroImage 128 (March 2016): 193–208. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.12.041.
- Mutschler, Isabella, Birgit Wieckhorst, Andrea H. Meyer, Tina Schweizer, Markus Klarhöfer, Frank H. Wilhelm, Erich Seifritz, and Tonio Ball. “Who Gets Afraid in the MRI-Scanner? Neurogenetics of State-Anxiety Changes during an fMRI Experiment.” Neuroscience Letters 583 (November 7, 2014): 81–86. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2014.09.021.
- Derix, Johanna, Shan Yang, Falk Lüsebrink, Lukas Dominique Josef Fiederer, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, Ad Aertsen, Oliver Speck, and Tonio Ball. “Visualization of the Amygdalo–hippocampal Border and Its Structural Variability by 7T and 3T Magnetic Resonance Imaging.” Human Brain Mapping 35, no. 9 (September 1, 2014): 4316–29. doi:10.1002/hbm.22477.
- Mutschler, Isabella, Tonio Ball, Johanna Wankerl, and Irina A. Strigo. “Pain and Emotion in the Insular Cortex: Evidence for Functional Reorganization in Major Depression.” Neuroscience Letters, Neuroimaging of Pain: Insights into normal and pathological pain mechanisms, 520, no. 2 (June 29, 2012): 204–9. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.03.095.
- Dümpelmann, Matthias, Tonio Ball, and Andreas Schulze-Bonhage. “sLORETA Allows Reliable Distributed Source Reconstruction Based on Subdural Strip and Grid Recordings.” Human Brain Mapping 33, no. 5 (May 1, 2012): 1172–88. doi:10.1002/hbm.21276.
- Ball, Tonio, Thomas P. K Breckel, Isabella Mutschler, Ad Aertsen, Andreas Schulze‐Bonhage, Jürgen Hennig, and Oliver Speck. “Variability of fMRI‐response Patterns at Different Spatial Observation Scales.” Human Brain Mapping 33, no. 5 (May 1, 2012): 1155–71. doi:10.1002/hbm.21274.
- Mutschler, Isabella, Birgit Wieckhorst, Oliver Speck, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, Jürgen Hennig, Erich Seifritz, and Tonio Ball. “Time Scales of Auditory Habituation in the Amygdala.” Cerebral Cortex 20, no. 11 (November 1, 2010): 2531–39. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq001.
- Wieckhorst, B, I Mutschler, A Schulze-Bonhage, J Hennig, E Seifritz, O Speck, and T Ball. “Habituation in the Human Amygdala and Its Subregions Investigated Using High Resolution Functional MRI.” NeuroImage, Organization for Human Brain Mapping 2009 Annual Meeting, 47, Supplement 1 (July 2009): S106. doi:10.1016/S1053-8119(09)70937-1.
- Mutschler, Isabella, Birgit Wieckhorst, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, Erich Seifritz, Jürgen Hennig, Oliver Speck, and Tonio Ball. “Probabilistic Assignment of Brain Responses to the Human Amygdala and Its Subregions Using High Resolution Functional MRI.” In 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, edited by Jos Vander Sloten, Pascal Verdonck, Marc Nyssen, and Jens Haueisen, 807–10. IFMBE Proceedings. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-89208-3_193.
- Mutschler, Isabella, Birgit Wieckhorst, Sandra Kowalevski, Johanna Derix, Johanna Wentlandt, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, and Tonio Ball. “Functional Organization of the Human Anterior Insular Cortex.” Neuroscience Letters 457, no. 2 (June 26, 2009): 66–70. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.101.
- Ball, Tonio, Johanna Derix, Johanna Wentlandt, Birgit Wieckhorst, Oliver Speck, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, and Isabella Mutschler. “Anatomical Specificity of Functional Amygdala Imaging of Responses to Stimuli with Positive and Negative Emotional Valence.” Journal of Neuroscience Methods 180, no. 1 (May 30, 2009): 57–70. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.02.022.
- Ball, Tonio, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, Ad Aertsen, and Carsten Mehring. “Differential Representation of Arm Movement Direction in Relation to Cortical Anatomy and Function.” Journal of Neural Engineering 6, no. 1 (February 5, 2009): 016006. doi:10.1088/1741-2560/6/1/016006.
- Ball, Tonio, I. Mutschler, D. Jäger, M. Otte, A. Schulze-Bonhage, J. Hennig, O. Speck, and A. Schreiber. “Elastic Registration of Functional MRI Data to Sensorimotor Cortex.” In 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, edited by Jos Vander Sloten, Pascal Verdonck, Marc Nyssen, and Jens Haueisen, 684–88. IFMBE Proceedings 22. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-89208-3_163.
- Mutschler, Isabella, Birgit Wieckhorst, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, Erich Seifritz, Jürgen Hennig, Oliver Speck, and Tonio Ball. “Probabilistic Assignment of Brain Responses to the Human Amygdala and Its Subregions Using High Resolution Functional MRI.” In 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, edited by Jos Vander Sloten, Pascal Verdonck, Marc Nyssen, and Jens Haueisen, 807–10. IFMBE Proceedings. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-89208-3_193.
- Ball, Tonio, Benjamin Rahm, Simon B. Eickhoff, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, Oliver Speck, and Isabella Mutschler. “Response Properties of Human Amygdala Subregions: Evidence Based on Functional MRI Combined with Probabilistic Anatomical Maps.” PLoS ONE 2, no. 3 (March 21, 2007): e307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000307.
- Mutschler, I, T Ball, V Glauche, E Demandt, O Speck, and A Schulze-Bonhage. “Eine Untersuchung der neuronalen Grundlagen der Assoziation einer motorischen Handlung mit einem handlungsbezogenen Geräusch.” Klinische Neurophysiologie 38, no. 01 (March 2007). doi:10.1055/s-2007-976436.
- Ball, T, Tpk Breckel, A Schulze-Bonhage, O Speck, A Aertsen, and I Mutschler. “„Peak Quality Maps“ für Gruppenergebnisse basierend auf funktioneller Magnetresonanztomographie.” Klinische Neurophysiologie 38, no. 01 (March 2007). doi:10.1055/s-2007-976305.
- Breckel, Tpk, I Mutschler, O Speck, A Aertsen, A Schulze-Bonhage, and T Ball. “Zur Bedeutung der räumlichen Glättung von funktionellen magnetresonanztomographischen Daten für deren Korrelation mit probabilistisch definierten sensomotorischen und visuellen kortikalen Arealen.” Klinische Neurophysiologie 38, no. 01 (March 2007). doi:10.1055/s-2007-976438.
- Mutschler, Isabella, Andreas Schulze-Bonhage, Volkmar Glauche, Evariste Demandt, Oliver Speck, and Tonio Ball. “A Rapid Sound-Action Association Effect in Human Insular Cortex.” PLoS ONE 2, no. 2 (February 28, 2007): e259. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000259.
- Ball, Tonio. “Motorische Gehirnaktivität beim Menschen : eine Studie mittels Stromdichterekonstruktion und funktioneller MRT,” 2004. http://www.freidok.uni-freiburg.de/volltexte/1751/.
- Ball, Tonio, Axel Schreiber, Bernd Feige, Michael Wagner, Carl Hermann Lücking, and Rumyana Kristeva-Feige. “The Role of Higher-Order Motor Areas in Voluntary Movement as Revealed by High-Resolution EEG and fMRI.” NeuroImage 10, no. 6 (December 1999): 682–94. doi:10.1006/nimg.1999.0507.
- Schreiber, A., T. Ball, R. Kristeva-Feige, T. Mergner, B. Feige, R. Scheremet, C. H. Lucking, and J. Hennig. Primary and Secondary Motor Areas in fMRI and EEG, 1998. http://cds.ismrm.org/ismrm-1998/PDF6/p1568.pdf.
- Ball, T., R. Kristeva-Feige, T. Muller, M. Wagner, and C.H. Lucking. “Current Density Source Reconstruction of Movement-Related Potentials Using High-Resolution Electroencephalography.” Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 103, no. 1 (July 1, 1997): 78–78. doi:10.1016/S0013-4694(97)88302-6.
